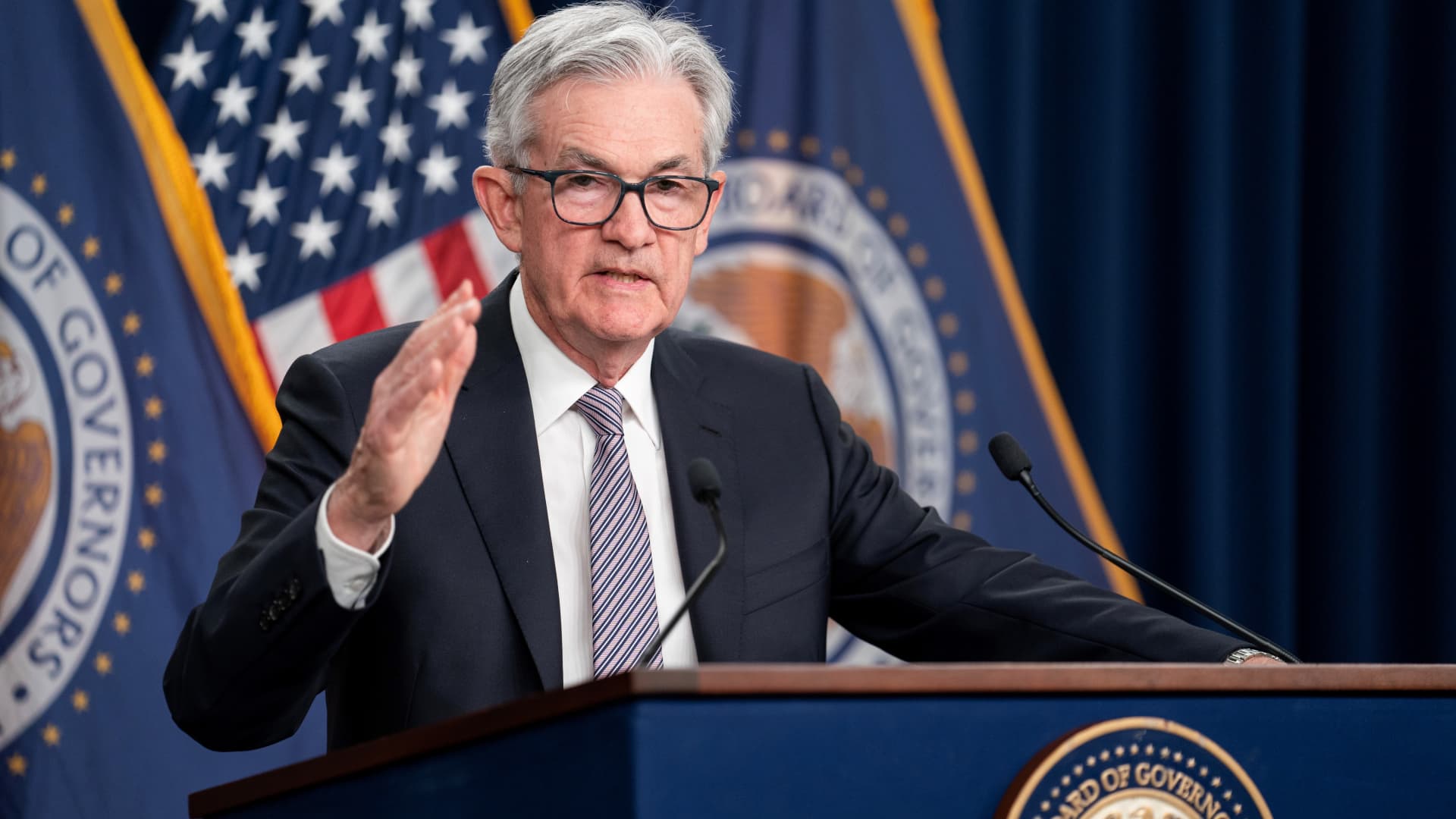
The Federal Reserve announced on Wednesday that it would maintain its key interest rate at the current range between 5.25% and 5.5% for the third consecutive time, citing low inflation and a stable economy. The decision was unanimous among policymakers on the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). However, the committee hinted at potential rate cuts in 2024, with at least three reductions anticipated.
The market had largely anticipated this decision, leading to a positive response in stock markets. The Dow Jones Industrial Average jumped over 400 points after the announcement.
The FOMC’s “dot plot” projections indicate the possibility of another four rate reductions in 2025, totaling a full percentage point. The committee envisions three additional cuts in 2026, bringing the fed funds rate to a range between 2% and 2.25%. While the FOMC indicated a gradual rate-cutting pace, the market priced in a more aggressive path, expecting a 1.5 percentage point cut in 2024, twice the FOMC’s suggested rate.
The statement following the meeting emphasized that the committee would consider various factors before deciding on “any” policy tightening, a term not previously used. This potentially signals a shift away from the tightening stance.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell mentioned that inflation has decreased from its peak, and economic growth remains positive. The Fed’s preferred inflation gauge is expected to meet the central bank’s 2% target in the coming months.
Despite a positive economic outlook, the FOMC is open to policy adjustments, considering the impact of previous tightening measures. The Fed aims to strike a balance between addressing inflation concerns and supporting economic growth. The decision also comes amid political considerations, with persistently high prices affecting President Joe Biden’s approval ratings. The Fed’s cautious approach is aligned with monitoring data and adjusting policies accordingly.